





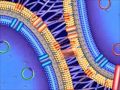


























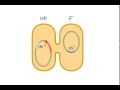
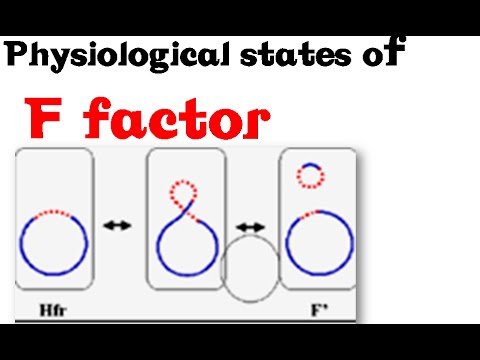



































One way of transferring resistance, however, is for that genetic recipe to be neatly written into a sharable book of sorts called a plasmid, which is then picked up and read by a neighboring bacteria through a process called conjugation. As resistance to antibiotics grows around the world, scientists are trying to figure out how to stop it from spreading. Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of a copy of a plasmid from one bacterial cell to another. In this experiment you'll allow conjugation to occur, then verify that it occured both by checking for the transfer of antibiotic resistance from one cell to another and by directly examining the cells' DNA. Gene transfer results in genetic variation in bacteria and is a large problem when it comes to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes. Ways for bacteria to share their genes: Conjugation: Two bacteria can pair up and connect through structures in the cell membranes and then transfer DNA from one bacterial cell to another. Bacterial conjugation and transfer of F plasmid Conjugative plasmid transfer themselves between bacteria, which had lead to spread of antibiotic resistance among pathogenic bacteria. Before talking about the mechanism of conjugation lets let’s first remind some of the key information related to plasmid. The process of bacterial conjugation is based on the principle that the plasmid or any other genetic material is transferred from the donor cell to the recipient cell through close physical contact. Of all the conjugative plasmids, the F (fertility) plasmid of E. coli was the first discovered and is one of the best-studied. As shown in the animation, a bacterium can directly transfer genetic material to another bacterium using a structure called a pilus. This cell-to-cell transfer process, called conjugation, helps antibiotic resistance genes spread quickly throughout a bacterial population. This animation is a clip from a 1999 Holiday Lecture Series, 2000 and Beyond: ... Conjugation is a common mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria that is instrumental in the spread of antibiotic resistance among bacteria. Most resistance genes are found on mobile genetic elements and primarily spread by conjugation. Bacterial Conjugation. Bacterial conjugation is one of the principal means of dissemination of genetic information among microbes and from bacteria to other domains of life including plants and other eukaryotes. From: Encyclopedia of Microbiology (Third Edition), 2009. Related terms: Plasmid; Nested Gene; Bacterium; Conjugation; Mutation; Bacteriophage Start studying Lab 2 - Bacterial Conjugation and Drug Resistance. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of antibiotic resistance genes has received increased scrutiny from the scientific community in recent years owing to the public health threat associated with antibiotic resistant bacteria. Most studies have examined HGT in growing cultures. We examined conjugation in growing and non-growing cultures of E. coli using a conjugative multi antibiotic and metal ...
[index] [3775] [1856] [4620] [8163] [4011] [6980] [3651] [8475] [5717] [9055]
Copyright © 2024 m.bk0info.site